ADVERTISEMENT
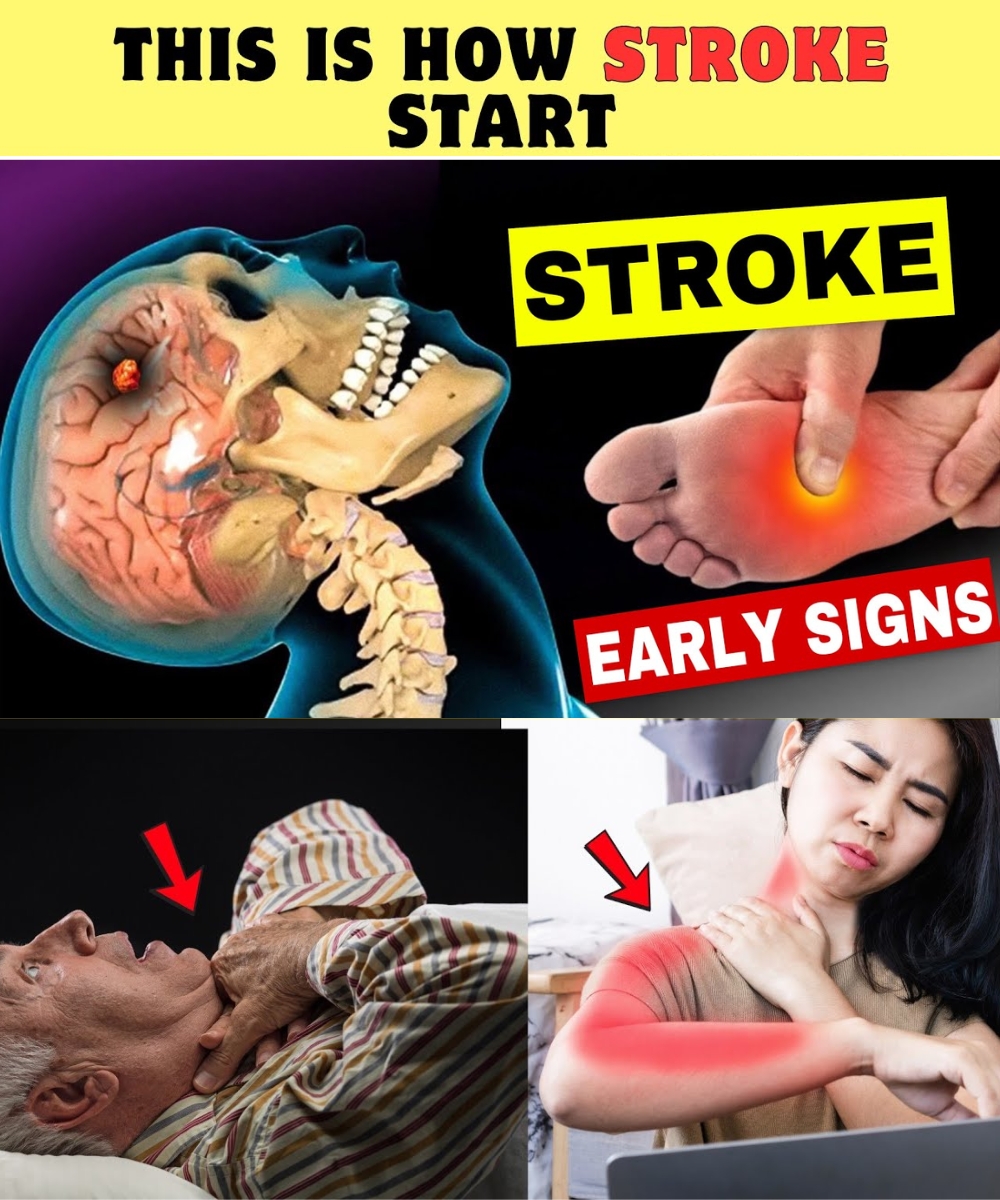
A stroke happens when the blood supply to a section of the brain becomes blocked or drastically reduced. When this occurs, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and essential nutrients, causing them to die within minutes. While emergency treatment is absolutely critical once a stroke begins, many people don’t realize that the body often gives early signals days or even weeks in advance. Recognizing these signs can give you the chance to take action early — and potentially avoid a life-threatening event altogether.
1. Frequent or Unusual Headaches
Regular headaches are common, but if you start experiencing headaches that are new, unusually intense, or noticeably different from your typical pattern, this could indicate restricted blood flow in the brain. These headaches may appear repeatedly and don’t always respond to medication, making them a possible early warning sign.
2. Dizziness or Difficulty Maintaining Balance
If you suddenly find yourself feeling unsteady, lightheaded, or unable to maintain your balance without any clear reason, it may be more than simple fatigue. Persistent dizziness can signal a problem with blood circulation to areas of the brain responsible for coordination and movement.
3. Sudden and Unexplained Fatigue
Feeling tired is normal, but extreme exhaustion that strikes out of nowhere — even after adequate rest — should be taken seriously. When the brain isn’t receiving enough oxygen, it often results in overwhelming tiredness, which can be a precursor to a stroke.
4. Problems With Vision
Any unexpected changes in eyesight, such as double vision, blurred vision, or partial blindness in one eye, might indicate a developing stroke. These vision disruptions suggest that the parts of the brain involved in sight may not be getting proper blood flow.
5. Trouble Speaking or Understanding Others
If you suddenly find your speech slurred, have difficulty pronouncing words, or struggle to comprehend what others are saying, you should consider this a significant warning sign. These communication difficulties often occur during mini-strokes (TIAs), which commonly precede major strokes.
6. Weakness or Numbness, Especially on One Side
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT